What are skin lesions?
Skin lesions are areas of the skin that look or feel different from the surrounding tissue. They can appear as bumps, sores, discoloration, or rashes and can be caused by conditions ranging from minor irritations to serious disorders. Primary skin lesions are those that appear directly due to a specific condition, while secondary lesions evolve from primary ones or occur due to external factors like scratching or infection.
When should I be concerned about a skin lesion?
You should be concerned if a skin lesion changes in size, shape, color, or texture, or if it becomes painful, itchy, or bleeds. Lesions that persist longer than a few weeks without improvement or continue growing should also be evaluated. Prompt attention is particularly important for lesions on the face or areas exposed to the sun, as they could indicate malignant skin lesions or skin cancer.
What does a skin lesion look like?
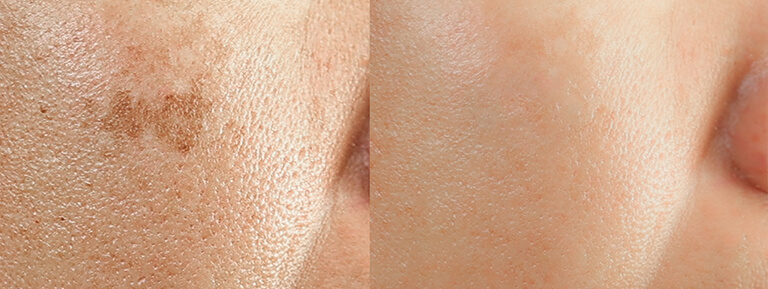
Skin lesions vary significantly in appearance, ranging from red patches, raised bumps, blisters, or flat spots to scaly or crusty areas. Some lesions may be flesh-colored, while others can appear dark, red, or white. Because skin lesions pictures can show diverse characteristics, any unusual or persistent changes in your skin’s appearance should be professionally evaluated.
What causes skin lesions on the body?
Skin lesions can result from numerous causes, including infections, allergic reactions, sun exposure, autoimmune disorders, diabetes, or even cancer. Diabetic skin lesions, for example, commonly appear due to poor circulation and elevated blood sugar levels. Skin disorders like eczema, psoriasis, and dermatitis also commonly produce various types of lesions.
Can skin lesions go away?
Yes, many skin lesions can go away on their own, especially those caused by temporary factors like allergic reactions, minor injuries, or infections. However, some lesions, particularly those associated with chronic conditions or serious underlying health issues, may persist and require medical intervention. It’s important to seek evaluation if a lesion doesn’t improve over time.
Can lesions turn into cancer?
Certain skin lesions, particularly those exposed to UV radiation or associated with genetic predispositions, can indeed develop into cancer. Malignant skin lesions often exhibit irregular borders, uneven coloration, rapid growth, or frequent bleeding. Early detection through regular skin checks can help identify precancerous or cancerous lesions before they progress.
How long do skin lesions last?
The duration of skin lesions depends greatly on their underlying cause. Temporary conditions like insect bites or minor allergic reactions usually resolve within days to weeks. Conversely, chronic conditions or malignant lesions may persist indefinitely until treated. Consulting a medical professional can help determine the nature of your lesion and appropriate skin lesions treatment options.
What makes a skin lesion suspicious?
A lesion becomes suspicious when it exhibits rapid or continuous changes in color, size, shape, or texture. Characteristics like asymmetry, uneven edges, multiple colors within one lesion, or lesions larger than a pencil eraser are considered warning signs. Additionally, lesions that repeatedly bleed, itch, or fail to heal warrant prompt dermatological evaluation.
When should a skin lesion be removed?
Skin lesions should be removed if they pose a health risk, such as being precancerous or malignant, or if they cause discomfort or affect your appearance significantly. Removal may also be recommended for lesions prone to frequent irritation or infection. Treatment decisions depend on individual assessments and may involve various methods like surgical excision or laser treatments.
Why are skin lesions concerning?
Skin lesions are concerning because they may indicate underlying medical conditions, including infections, autoimmune disorders, or skin cancer. Early diagnosis and treatment of concerning lesions can prevent complications and significantly improve treatment outcomes. Regular skin checks are critical, especially if you have risk factors such as excessive sun exposure, family history of skin cancer, or chronic skin disorders.
What are the 10 skin lesions?
Ten common types of skin lesions include macules (flat spots), papules (small raised bumps), nodules (larger, firm lumps), pustules (pus-filled bumps), vesicles (small fluid-filled blisters), bullae (large blisters), plaques (thickened, raised areas), wheals (raised, itchy areas), scales (dry, flaky skin patches), and ulcers (open sores). Each type can indicate different underlying skin disorders or conditions.
How do you characterize skin lesions?
Skin lesions are characterized by factors including size, shape, color, texture, and location. Dermatologists consider whether lesions are raised or flat, smooth or rough, painful or painless, and isolated or clustered. Proper characterization helps determine potential causes, guides diagnostic testing, and informs effective skin lesions cure or management strategies.